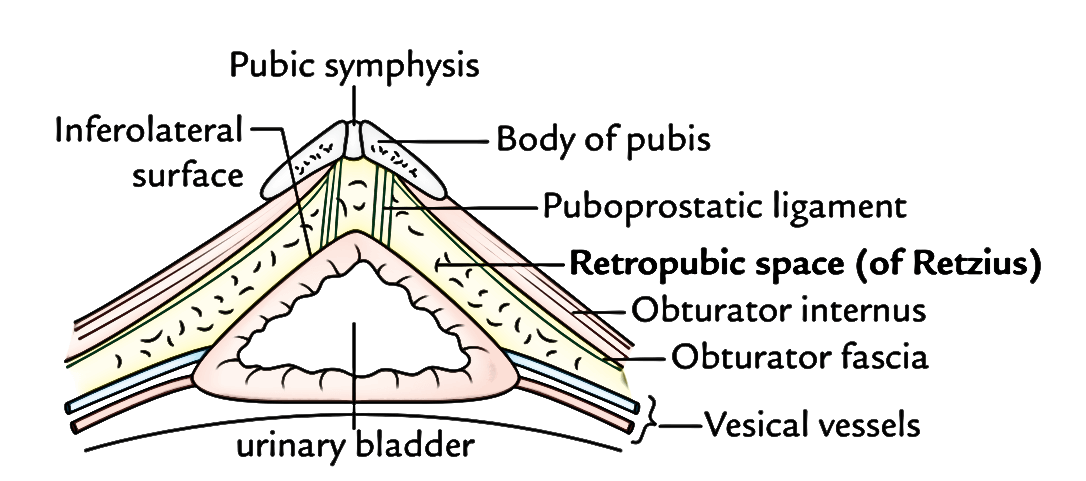
True And False Ligaments Of Urinary Bladder

Histology cross section of a normal guinea pig bladder (© RVC 2008) • It is a hollow, muscular organ • It is divided for descriptive purposes into three parts • Cranial Pole • Intermediate body • Caudal neck • Its wall comprises a muscle layer covered in transitional epithelium. • Its size and posistion are determined by how full it is. • When empty the bladder wall is wrinkled and thicker • It rests on the pubic bones • It is entirely in the pelvis of the large species but partly enters the abdomen of the carnivores • It is largely retroperitoneal in the larger species • When full and distended the folds disappear and the wall appears thinner • It then becomes intraperitoneal in the larger species • The trigone of the bladder gets its name as it looks like a triangle without a base. Hard knock life vol 2 rar. • It is of clinical importance and is formed by the paired uteric folds • These form by the orifice of the ureters • It is visible even when the bladder is full • The folds extend from the urethral opening to the neck of the bladder • Where they merge to form the urethral crest • It is believed to have increased sensitivty and is of differant embryological origin to the rest of tissue. More details can be found Muscles of the Bladder. A schematic overview of the lower urinary tract showing the innervation and muscles of the bladder The three muscular components of the bladder described below play a pivotal part in the Detrusor Muscle This network of smooth muscle fibres lie in three sheets within the bladder wall and are supplied by both parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves.
It is responsible for storage and expression of urine from the bladder. Parasympathetic Supply - Detrusor Muscle • S1-S3 • Synapse in pelvic plexus or bladder wall • Pelvic nerves • Innvervate the detrusor muscle • Action - excitatory • Function - empty bladder Sympathetic Supply - Detrusor Muscle • L1-L4 • Syanpse in caudal mesenteric ganglion - bladder wall • Hypogastric nerve • Receptor - beta 2 • Inhibitory action • Allows bladder filling Internal Urethral Sphincter A thickening of the bladder musculature found at the neck of the bladder which is continuous with the detrusor and is therefore smooth muscle. However, unlike the detrusor its innervation is purely from sympathetic fibres. Sympathetic Supply - Internal Urethral Sphincter • L1-L4 • Synapse in caudal mesenteric ganglion • Hypogastric nerve • Receptor - alpha 1 • Excitatory action • Function - retain urine through increased urethral tone External Urethral Sphincter This third component is more appropriately included in the anatomy section of the. The Ligaments of the Bladder • Two lateral ligaments • Insert in the dorsal abdominal wall • Within them are the residual umbilical vessels which still have some patency and convey small amounts of blood to the cranial bladder • They attach onto the bladder wall at the lateral vesical folds. • Median ligament • Connects the bladder to pelvic floor and linea alba • Attaches into the bladder at the median vesical fold • In the foetus this ligament supports the urachus.